by Dr. Saurabh Purohit and Dr. Imran Khan YD
What is a Riparian Ecotone?
The term “riparian” is derived from the Latin word riparius, which refers to land adjacent to a body of water. Riparian Ecotones are zones of transition between riverine and terrestrial ecosystems. They are highly productive and diverse due to the presence of water and nutrients and consequently, are far more effective in mitigating the negative effects of frequent water level fluctuations. Because of their ecotone characteristics and distinct ecological functions, the functions, products, and services provided by Riparian Ecotones are disproportionately numerous to their total surface area in the landscape.

Riparian Ecotones as a NbS (Nature- based Solution) for River Health Improvement
Riparian Ecotones have a significant impact on the microclimate of the region due to its effect on climatic parameters (precipitation, temperature, humidity, etc.). They act as ecological engineers by improving river health through a variety of ecosystem services. Specifically: –
- Riparian vegetation filters pollutants naturally, and densely vegetated riparian zones protect stream water quality through sediment and nutrient filtration.
- Riparian vegetation root network improve apparent soil cohesiveness and stream bank stability through a combination of mechanical and hydrologic impacts. Litter and debris from riparian vegetation increase channel roughness and reduce flowing water’s capacity for stream bank erosion.
- The temperature of the river is modulated by riparian vegetation, which blocks solar insolation and provides a cooling effect beneath the canopy.
- By regulating nutrient flux, Riparian Ecotones ensures food security in riverine ecosystems. They help to maintain hydrological conditions in watersheds by facilitating the exchange of surface and groundwater, which has a significant impact on ecological processes in small/narrow streams.
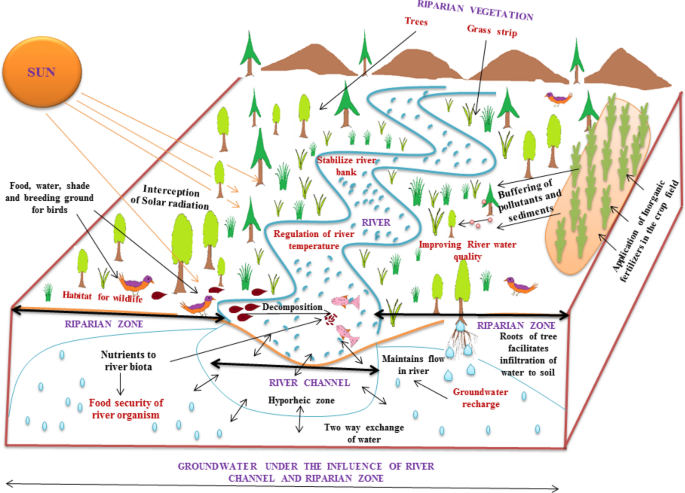
- They promote floral and faunal diversity by disseminating and propagating through various agents (wind, water, and animals), which play an important role in maintaining high species richness and endemism.
- They serve as corridors for the movement of flora and fauna between ecosystems. In addition, many native birds, fish, and invertebrates use it for shelter, feeding, and spawning.
- They also serve as an important source of income in rural areas.

A healthy Riparian Ecotone also serves as a popular recreational area, with common activities including fishing, swimming, boating, picnicking, and bird watching. People prefer to stay near these Ecotones because it makes them feel relaxed. Many religions hold spiritual significance for these locations. Many meditation or healing centres were located near the riverbank in the past, evoking the spiritual connection between humans and nature.
Riparian Ecotones are expected to be crucial in determining how vulnerable human and environmental systems are to climate change and how well-equipped they are to adapt in the twenty-first century. Because of their continuous evolution under high environmental variability in response to climate change, these ecotones have relatively high adaptive capacity. The high inter- and intra-connectivity of Riparian Ecotones, as well as its wide dispersal via different agents (wind, water, and animals), increases their adaptive capacity. Furthermore, the riparian biota’s dynamic nature allows it to respond more effectively to changing fluvial disturbances and the effects of climate change. When temperatures rise in aquatic and terrestrial environments, the role of riparian vegetation, for example, in providing thermal refuges for biota, becomes more important. Corridors for biota movement may become more important as organisms seek migration routes in response to changing environmental conditions.
Major Threats to Riparian Ecotones
Riparian Ecotones are affected by both man-made and natural disturbances. The destruction of these ecotones is caused by unrestricted agriculture growth and the free grazing of livestock. The fragmentation of Riparian Ecotones is also caused by the unregulated growth of cities. Human actions (like dams and flood control projects) that change the natural flow of water can make it harder for native riparian plants to grow and make it easier for non-native species to move in and take over. Human actions like cutting down trees, using groundwater, and mining change the structure, function, and services of Riparian Ecotones, as well as their ability to recover. Pesticides, industrial waste, sewage, and agricultural runoff are the major anthropogenic causes of heavy pollution in riparian habitats.
Many ecological processes in Riparian Ecotones will be affected by climate change because changes in the riparian zone and the land around it will affect them. Adversities of climate change like unpredictable rain, flash floods, and landslides make the situation even worse. The destruction of Riparian Ecotones has detrimental impacts on the habitat of flora and fauna and local climatic conditions. The local community’s way of life is also affected by how much they depend on the Riparian Ecotones.
Managing Riparian Ecotones sustainably
Integrating technical, environmental, economic, and social factors can help Riparian Ecotones be managed in a sustainable manner. A quantitative assessment of riparian vegetation is a keyway to figure out how healthy riparian areas are. Community-based natural resource management (CBNRM) can help restore Riparian Ecotones and aim for long-term sustainability by letting many stakeholders help make decisions.
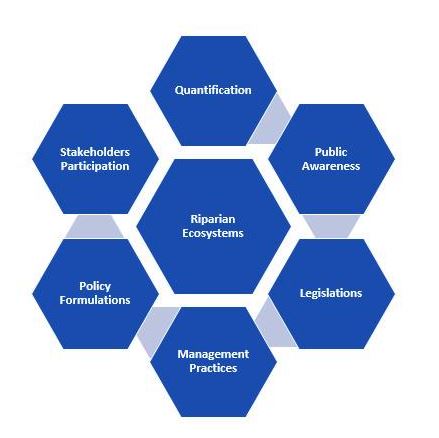
For Riparian Ecotones to be managed and kept in good shape, the local population needs to be thoroughly apprised of their importance. Streambank fencing, riparian buffer strips, rotational grazing, and organic farming are all technical interventions that can be used to manage riparian ecosystems in a healthy manner. Also, Riparian Ecotones’ loss and degradation can be slowed down by coming up with the right policies and making sure that existing environmental laws are followed.
References
Singh, R., Tiwari, A. K. and Singh, G. S. (2021) ‘Managing riparian zones for river health improvement: an integrated approach’, Landscape and Ecological Engineering, 17(2), pp. 195–223. doi: 10.1007/s11355-020-00436-5.
For Further Reading
- What are Riparian Ecosystems?
- An overview of riparian systems and potential problems.
- Sharma, S., Agrawal, M., Roy, A. (2021). Riparian https://www.earth.com/earthpedia-articles/what-are-riparian- ecosystemsEcotones: An Important Derivative for
Managing River Pollution. In: Singh, A., Agrawal, M., Agrawal, S.B. (eds) Water Pollution and
Management Practices. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8358-2_9 - Kujur, E., Jhariya, M.K., Yadav, D.K. et al. Phytosociological attributes and regeneration
potential of riparian vegetation in Northern Chhattisgarh, India. Environ Dev Sustain 24,
2861–2886 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01557-z - Verry, E.S., Dolloff, C.A. & Manning, M.E. Riparian ecotone: A functional definition and
delineation for resource assessment. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution: Focus 4, 67–94 (2004).






1 thought on “Riparian Ecotones and Why Conserving them is Absolutely Essential”
It seems that the transition area is one type of wetland.
Comments are closed.