The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) has predicted a normal monsoon for 2023, estimating rainfall at 96% of the long-term average. Despite this, the IMD also cautions that El Niño conditions are likely to emerge during the monsoon season. In a recent update, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has similarly noted an increasing likelihood of El Niño forming later in the year.

This development would result in a shift in weather and climate patterns across various regions worldwide, presenting a stark contrast to the enduring effects of La Niña. As a consequence, this shift is expected to drive an increase in global temperatures. With that in mind, it is essential to understand the El Niño and La Niña phenomena and the potential impacts they may have on India, particularly in rural areas.
Understanding El Niño and La Niña
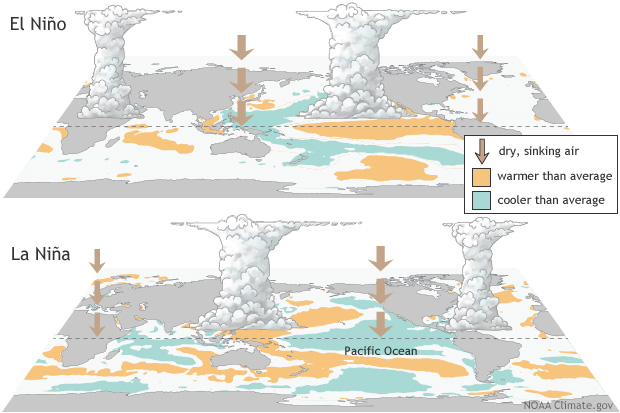
El Niño and La Niña are complex, naturally occurring climate phenomena that have far-reaching consequences on weather patterns around the world. They are part of a larger climate system called the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), which originates in the tropical Pacific Ocean.
El Niño: Warming Waters in the Tropical Pacific
El Niño is characterized by the warming of surface waters in the eastern and central Pacific Ocean. The term “El Niño” is derived from the Spanish term for “the child,” as these events often occur around Christmas time. This warming typically lasts for several months to a year and disrupts the normal ocean-atmosphere interactions in the region.
Under normal conditions, the trade winds blow from east to west across the Pacific, pushing warm surface waters towards the western Pacific. This causes cold water to upwell from the deep ocean in the east, leading to a temperature gradient across the Pacific. However, during an El Niño event, the trade winds weaken or even reverse, causing warm water to build up in the eastern Pacific. This leads to a host of changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation patterns, impacting the climate in various regions around the world.
La Niña: Cooling Waters in the Tropical Pacific
La Niña, on the other hand, is characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific. The name “La Niña” translates to “the girl” in Spanish, and it is considered the counterpart of El Niño. While El Niño events are marked by the weakening of trade winds, La Niña events involve the strengthening of these winds. This results in even greater upwelling of cold water in the eastern Pacific, further enhancing the temperature gradient across the ocean.
Just like El Niño, La Niña can also lead to significant changes in global weather patterns, though the effects are often opposite to those of El Niño.
El Niño’s Impact on Rural India
El Niño events can have severe consequences for agriculture, water resources, and overall livelihood in rural India. Here are some of the keyways in which El Niño affects rural India:
1. Droughts and Monsoon Failure
India’s agricultural sector is heavily dependent on the Southwest Monsoon, which provides around 75% of the country’s annual rainfall. However, El Niño events are often associated with weaker monsoons, leading to reduced rainfall and drought-like conditions in many parts of the country. As a result, crop production can suffer significantly, threatening the food security of millions of people.
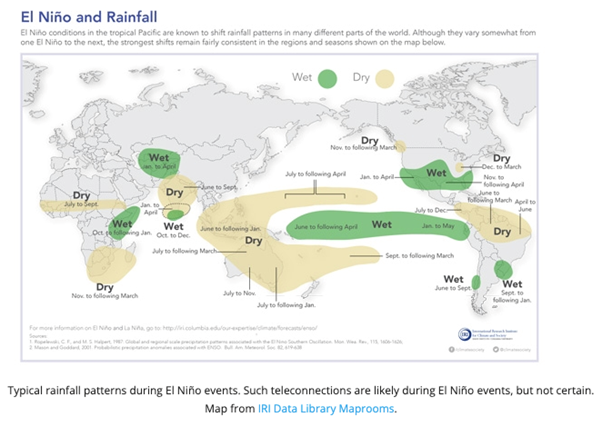
2. Increased Risk of Heatwaves
El Niño events can also lead to unusually high temperatures in rural India. The buildup of heat, combined with dry conditions due to failed monsoons, can result in devastating heatwaves. These heatwaves can be particularly harmful to vulnerable populations in rural areas, who often lack access to proper shelter and cooling facilities.
3. Impact on Water Resources
Reduced rainfall during El Niño events can strain water resources in rural India. Many rural communities rely on surface water sources like rivers and reservoirs for drinking water and irrigation. With reduced rainfall, these sources can dry up or become severely depleted, leading to water scarcity and affecting the quality of life in rural areas.
4. Economic Consequences
El Niño’s impact on agriculture and water resources can have severe economic consequences for rural India. Crop failure can lead to loss of income for farmers and increased food prices. Additionally, water scarcity can affect industries that rely on water, such as agriculture, livestock, and fisheries, further exacerbating economic hardships in rural communities.
5. Health Implications
The combination of drought, heatwaves, and water scarcity can also have serious health implications for rural populations. Waterborne diseases, such as cholera and dysentery, can become more prevalent due to contaminated water sources. Furthermore, malnutrition can become a major concern due to reduced food availability, particularly affecting children and pregnant women.

6. Migration and Social Issues
El Niño-induced hardships in rural India can lead to increased migration to urban areas, as people search for better opportunities and living conditions. This can result in overcrowded cities, strained resources, and increased social tensions.
Mitigation Measures
To reduce the impact of El Niño events on rural India, several mitigation measures can be implemented:
1. Improved Weather Forecasting
Enhancing the accuracy of weather forecasting can help predict El Niño events and their potential impact on the monsoon. This can enable better preparedness, allowing farmers to plan their crops accordingly and governments to implement appropriate water management policies.
Read: Role of Mobile Apps for Climate Smart Agro-Advisory in Agriculture
2. Diversification of Agriculture
Encouraging farmers to diversify their crops and adopt drought-resistant varieties can help reduce the impact of El Niño on food security. Additionally, promoting sustainable agricultural practices, such as rainwater harvesting and efficient irrigation systems, can help conserve water and improve productivity.
Read: Why Climate Resilient Agriculture is Critical for Food Security in India
3. Strengthening Water Infrastructure and Water Governance
Investing in improved water infrastructure, such as dams, reservoirs, and canals, can help store and distribute water more efficiently during times of scarcity. On the other hand, addressing behavioural change through initiatives like water budgeting, water stewardship and water governance will aid communities in dealing with climate variabilities.
4. Community Awareness and Capacity Building
Educating rural communities about the potential impacts of El Niño and building their capacity to respond to such events can go a long way in reducing vulnerability. This can include training in water management, sustainable agriculture, and disaster preparedness.
5. Social Safety Nets
Establishing social safety nets, such as food and cash transfer programs, can help protect vulnerable populations from the economic and health impacts of El Niño-induced hardships.
The El Niño and La Niña are critical climate phenomena that can have far-reaching consequences on global weather patterns, including those in rural India. By understanding these events and implementing appropriate mitigation measures, it is possible to minimize their negative impacts and build resilience in vulnerable communities.